Yiddish leid
| Yiddish | |
|---|---|
| ייִדיש, יידיש or אידיש yidish/idish | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈjɪdɪʃ] or [ˈɪd ɪʃ] |
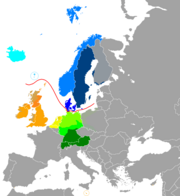
| Native tae | Central, Eastren an Wsstren Europe |
| Region | Europe, Israel, North Americae, ither regions wi Jewish populations[1] |
| Ethnicity | Ashkenazi Jews |
Native speakers | (1.5 million citit 1986–1991 + hauf undatit)[1] |
| Ebreu alphabet (Yiddish orthografie) | |
| Offeecial status | |
Recognised minority leid in | |
| Regulatit bi | Na formal bouks YIVO de facto |
| Leid codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | yi |
| ISO 639-2 | yid |
| ISO 639-3 | yid – inclusive codeIndividual codes: ydd – Eastren Yiddishyih – Wastren Yiddish |
| Glottolog | yidd1255[2] |
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB-g = 52-ACB-ga (Wast) + 52-ACB-gb (East); totallin 11 varieties |
Yiddish (ייִדיש yidish or אידיש idish, literally "Jewish") is an Ashkenazi Jewish leid o hie German oreegin, spaken ootthrough the warld. It developpit as a fusion o German dialects wi Ebreu, Aramaic, Slavic leids an traces o Romance leids.[3][4] It is written in the Ebreu alphabet.
The leid oreiginatit in the Ashkenazi cultur that developpit frae aboot the 10t century in the Rhineland an syne spreid till Central an Eastern Europe an hinderly tae ither continents. In the earliest remeenin mentions tae it, the leid is cawed לשון־אַשכּנז (loshn-ashknez = "Ashkenaz leid") an טײַטש (taytsh, a variant o tiutsch, the contemporar name for the leid itherweys spaken in the region o oreegin, nou cawed Middle Hie German; compare the modren New High German Deutsch). In common usage, the language is forby cried מאַמע־לשון (mame-loshn, literally "mither tongue"), distinguishing it frae Biblical Hebrew whilk is termed לשון־קודש (loshn-koydesh, "haly tongue") an Aramaic. The term "Yiddish" didnae become the maist frequent uised designation in the leid's literatur till the 18t century.
For a signeificant skare o its history, Yiddish wis the main spaken leid o the Ashkenazi Jews an ance spanned a braid dialect continuum frae Wastren Yiddish till three major groups athin Eastren Yiddish, namely Litvish, Poylish an Ukrainish. Eastren an Wastren Yiddish is maist parteilcuar distinguisht bi the conseitherable comprehension o wirds o Slavic oreegin in the Eastren dialects. While Wastren Yiddish haes few remainin speakers, Eastren dialects remeen in wide uise.
Yiddish is written an spaken in Orthodox Jewish commonties the warld ower. It is a hame language in maist Hasidic commonties, whaur it is the first leid learnt in bairnheid, uised in scuils an in mony social settins.
Yiddish is forby uised in the adjectival sense tae designate attributes o Ashkenazic cultur (for example, Yiddish keukin an Yiddish muisic).[5]
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- ↑ a b Yiddish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Eastren Yiddish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Wastren Yiddish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) - ↑ Nordhoff, Sebastian; Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2013). "Yiddish". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
- ↑ Introduction to Old Yiddish literature, p. 72, Baumgarten and Frakes, Oxford University Press, 2005
- ↑ "Development of Yiddish over the ages", www.jewishgen.org
- ↑ Oscar Levant descrived Cole Porter's 'My Heart Belongs to Daddy" as "ane o the maist Yiddish tunes eiver written" in maugre o "Cole Porter's genetic background" bein "completely alien tae ony Jewishness." Oscar Levant,The Unimportance of Being Oscar, Pocket Books 1969 (reprint of G.P. Putnam 1968), p. 32. ISBN 0-671-77104-3.
Freemit airtins
[eedit | eedit soorce]| Yiddish edeetion o Wikipaedia, the free encyclopaedia |
| Wikibooks haes a beuk on the topic o Yiddish |
| Wikibooks haes a beuk on the topic o Yiddish for Yeshivah Bachurim |
- Free Yiddish Dictionary Archived 2021-02-26 at the Wayback Machine
- Verterbukh – Yiddish Resources Online
- Jewish Language Research Website: Yiddish Archived 2006-02-08 at the Wayback Machine
- On-line Yiddish dictionary Archived 2006-02-02 at the Wayback Machine
- A Dictionary o the Yiddish Leid bi Alexander Harkavy, 1898 (frae Google Books)
- Yiddish Typewriter - interconverts Yiddish text in Hebrew script wi YIVO transliteration
- WWW Virtual Library History Central Catalogue - Yiddish Sources Academic portal for Yiddish Studies, includes an online bibliography.
- 'Hover & Hear' New York Yiddish pronunciations Archived 2009-01-26 at the Wayback Machine, an compare wi equivalents in Inglis an ither Germanic leids.
| Wikimedia Commons haes media relatit tae Yiddish language. |
| This Europe-relatit airticle is a stub. Ye can help Wikipaedia bi expandin it. |
| This leid-relatit airticle is a stub. Ye can help Wikipaedia bi expandin it. |