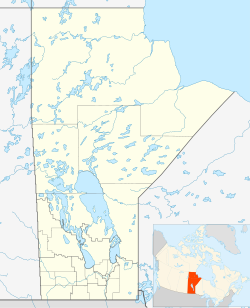
Winnipeg
Winnipeg (/[unsupported input]ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ/) is the caipital an lairgest ceety o Manitoba, Canadae, an is the primary municipality o the Winnipeg Caipital Region, wi mair nor 60% o Manitoba's population. It is locatit near the langitudinal centre o North Americae, at the confluence o the Red an Assiniboine Rivers (a pynt commonly kent as The Forks).
The name "Winnipeg" comes frae the Cree for "muddy waters". The Winnipeg aurie wis a tradin centre for Aboriginal fowks prior tae the arrival o Europeans. The first fort wis biggit thare in 1738 bi French traders.[3] A dounset wis later foondit bi the Selkirk settlers in 1812, the nucleus of which wis incorporatit as the City of Winnipeg in 1873. Durin the late 19t century an early 20t century, Winnipeg wis ane o the fastest growin ceeties in North Americae. The University o Manitoba, foondit durin this period, wis the first varsity in Wastren Canadae.
Winnipeg haes a diversified economy, wi sectors in finance, manufacturin, fuid an beverage production, cultur, retail an tourism. Winnipeg is a major transportation hub, served bi Richardson Internaitional Airport. The ceety haes railwey connections tae the Unitit States an Eastren an Wastren Canadae throu three Class I rail carriers.
Winnipeg is the seivent-lairgest municipality in Canadae, wi a population o 633,451 in the Canadae 2006 Census. The ceety's census metropolitan aurie, consistin o the ceety o Winnipeg, ten nearby rural municipalities an the First Naitions reserve o Brokenhead 4, Manitoba, is Canadae's aicht-lairgest, wi 694,668 indwallers. Winnipeg's cultural organisations an festivals include the ryal Winnipeg Ballet, Manitoba Opera, Le Cercle Molière, Festival du Voyageur an Folklorama. Professional sports organisations based in the ceety include the Winnipeg Blue Bombers, the Winnipeg Goldeyes, an the Manitoba Moose.
Sister ceeties
[eedit | eedit soorce]Winnipeg maintains tred development programs, cultural an educational pairtnerships in sister ceety agreements wi thir ceeties:
- 1970: Setagaya (Japan)
 [4]
[4] - 1971: Reykjavík (Iceland)
 [5]
[5] - 1973: Lviv (Ukraine)
 [5]
[5] - 1979: Manila (Philippines)
 [6]
[6] - 1982: Taichung (Taiwan)
 [7]
[7] - 1982: Kuopio (Finland)
 [8]
[8] - 1984: Beersheba (Israel)
 [9]
[9] - 1988: Chengdu (Fowkrepublic o Cheenae)
 [10]
[10] - 1992: Jinju (Republic o Korea)
 [11]
[11] - 1999: San Nicolás de los Garza (Mexico)
 [9]
[9]
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- ↑ "Population and dwelling counts, for Manitoba and census subdivisions (municipalities)". Statistics Canada, 2011 Census of Population. Retrieved 6 Apryle 2012.
- ↑ "Metropolitan areas of Manitoba". Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 Februar 2011.
- ↑ Champagne, Antoine (1968–69). "The Vérendryes and Their Successors, 1727-1760". MHS Transactions. 3 (25).CS1 maint: date format (link)
- ↑ "Setagaya's Sister Cities". Archived frae the original on 11 Juin 2008. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.
- ↑ a b "Winnipeg City Council Minutes for 1978" (PDF). Archived frae the original (PDF) on 28 August 2011. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.
- ↑ "About Us". The Filipino Journal. Archived frae the original on 7 Februar 2013. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.
- ↑ "Taichung City Diplomacy - Sister Cities". Taichung City Government. Archived frae the original on 5 Julie 2007. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.
- ↑ "Kuopion kaupunki". Archived frae the original on 24 Apryle 2008. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.
- ↑ a b "Task Force on Diversity" (PDF). City of Winnipeg. 2001. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.[deid airtin]
- ↑ "Winnipeg (Canada)". Foreign Affairs Office, Chengdu Municipality. Archived frae the original on 5 Mairch 2016. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.
- ↑ "Sister City". Korean Local Government. Retrieved 16 Julie 2009.[deid airtin]
| Wikimedia Commons haes media relatit tae Winnipeg. |
| This Canadae-relatit airticle is a stub. Ye can help Wikipaedia bi expandin it. |
| This ceity-relatit airticle is a stub. Ye can help Wikipaedia bi expandin it. |