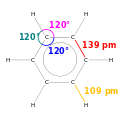Benzene
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Benzene
| |||
| Seestematic IUPAC name
Cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene | |||
| Ither names
1,3,5-Cyclohexatriene, Benzol, Phene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Nummer | 200-753-7 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS nummer | CY1400000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 78.11 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odour | Aromatic, petrol-like | ||
| Density | 0.8765(20) g/cm3[1] | ||
| Meltin pynt | 5.53 °C (41.95 °F; 278.68 K) | ||
| Bylin pynt | 80.1 °C (176.2 °F; 353.2 K) | ||
| 1.53 g/L (0 °C) 1.81 g/L (9 °C) 1.79 g/L (15 °C)[2][3][4] 1.84 g/L (30 °C) 2.26 g/L (61 °C) 3.94 g/L (100 °C) 21.7 g/kg (200 °C, 6.5 MPa) 17.8 g/kg (200 °C, 40 MPa)[5] | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, CHCl3, CCl4, diethyl ether, acetone, acetic acid[5] | ||
| Solubility in ethanediol | 5.83 g/100 g (20 °C) 6.61 g/100 g (40 °C) 7.61 g/100 g (60 °C)[5] | ||
| Solubility in ethanol | 20 °C, solution in water: 1.2 mL/L (20% v/v)[6] | ||
| Solubility in acetone | 20 °C, solution in water: 7.69 mL/L (38.46% v/v) 49.4 mL/L (62.5% v/v)[6] | ||
| Solubility in diethylene glycol | 52 g/100 g (20 °C)[5] | ||
| log P | 2.13 | ||
| Vapour pressur | 12.7 kPa (25 °C) 24.4 kPa (40 °C) 181 kPa (100 °C)[7] | ||
| λmax | 255 nm | ||
| Magnetic susceptibility | 54.8·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.5011 (20 °C) 1.4948 (30 °C)[5] | ||
| Viscosity | 0.7528 cP (10 °C) 0.6076 cP (25 °C) 0.4965 cP (40 °C) 0.3075 cP (80 °C) | ||
| Structur | |||
| Molecular shape | Tetrahedral | ||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Speceefic heat capacity, C | 134.8 J/mol·K | ||
| Staundart molar entropy S |
173.26 J/mol·K[7] | ||
| Std enthalpy o formation ΔfH |
48.7 kJ/mol | ||
| Std enthalpy o combustion ΔcH |
3267.6 kJ/mol[7] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |    [8] [8]
| ||
| GHS signal wird | Danger | ||
| GHS hazard statements | H225, H304, H315, H319, H340, H350, H372[8] | ||
| GHS precautionary statements | P201, P210, P301+310, P305+351+338, P308+313, P331[8] | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash pynt | −11.63 °C (11.07 °F; 261.52 K) | ||
| 497.78 °C (928.00 °F; 770.93 K) | |||
| Explosive leemits | 1.2–7.8% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (Median dose)
|
930 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| Relatit compoonds | |||
Except whaur itherwise notit, data are gien for materials in thair staundart state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Benzene is an organic chemical compoond wi the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is componed o sax caurbon atoms jynt in a ring wi ane hydrogen atom attached tae ilk. As it conteens anerly caurbon an hydrogen atoms, benzene is clessed as a hydrocaurbon.
Benzene is a naitural constituent o crude ile an is ane o the elementar petrochemicals. Due tae the cyclic conteenous pi bond atween the caurbon atoms, benzene is clessed as an aromatic hydrocarbon, the seicont [n]-annulene ([6]-annulene). It is whiles abbreviatit PhH. Benzene is a colourless an heichly flammable liquid wi a sweet smell, an is responsible for the aroma aroond petrol stations. It is uised primarily as a precursor tae the manufacture o chemicals wi mair complex structur, uic as ethylbenzene an cumene, o that billions o kilogrammes are produced annually. As benzene haes a heich octane nummer, aromatic derivatives lik toluene an xylene teepically comprise up tae 25% o petrol. Benzene itsel haes been leemitit tae less nor 1% in petrol acause it is a kent human carcinogen. Most nan-industrial applications hae been leemitit as weel for the same raison.
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- ↑ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ Arnold, D.; Plank, C.; Erickson, E.; Pike, F. (1958). "Solubility of Benzene in Water". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Chemical & Engineering Data Series. 3 (2): 253. doi:10.1021/i460004a016.
- ↑ Breslow, R.; Guo, T. (1990). "Surface tension measurements show that chaotropic salting-in denaturants are not just water-structure breakers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (1): 167–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87..167B. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.1.167. PMC 53221. PMID 2153285.
- ↑ Coker, A. Kayode; Ludwig, Ernest E. (2007). Ludwig's Applied Process Design for Chemical And Petrochemical Plants. 1. Elsevier. p. 114. ISBN 0-7506-7766-X. Retrieved 31 Mey 2012.
- ↑ a b c d e "Archived copy". Archived frae the original on 29 Mey 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ↑ a b Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1952). [Google Books Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds] Check
|url=value (help). Van Nostrand. Retrieved 29 Mey 2014. - ↑ a b c Benzene in Linstrom, P.J.; Mallard, W.G. (eds.) NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD. http://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved 2014-05-29)
- ↑ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Benzene. Retrieved on 2014-05-29.
- Pages with URL errors
- Pages uisin collapsible list wi both background an text-align in titlestyle
- Annulenes
- Simple aromatic rings
- IARC Group 1 carcinogens
- Sile contamination
- Hydrocarbon solvents
- Hazardous air pollutants
- Immunotoxins
- Mutagens
- Teratogens
- Occupational safety an heal
- Carcinogens
- Commodity chemicals
- Petrochemicals