Ibuprofen
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Tred names | Advil, Brufen, Motrin, Nurofen, etc. |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682159 |
| Leecence data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes o admeenistration | Oral, rectal, topical, an intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 49–73% |
| Protein bindin | 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C9) |
| Biological hauf-life | 1.8–2 h |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Nummer | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.152 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
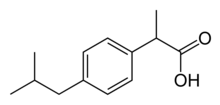
| Formula | C13H18O2 |
| Molar mass | 206.29 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Density | 1,03 gr/ml g/cm3 |
| Meltin pynt | 76 °C (169 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ibuprofen (INN) (/ˈaɪbjuːproʊfɛn/ or /aɪbjuːˈproʊfən/ EYE-bew-PROH-fən; from iso-butyl-propanoic-phenolic acid) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for pain relief, fever reduction,[1] and against swelling.
Ibuprofen has an antiplatelet effect, though relatively mild and somewhat short-lived compared with aspirin or prescription antiplatelet drugs. In general, ibuprofen has a vasodilation effect[2]. Ibuprofen is a 'core' medicine in the World Health Organization's Model List of Essential Medicines necessary that meet the minimum medical needs of a basic healthcare system.[3][4][5][6]
Ibuprofen was derived from propanoic acid by the research firm of Boots Group during the 1960s[7] and patented 1961. Orginal market as Brufen, ibuprofen is available under a variety of popular trademarks, including Motrin, Nurofen, Advil, Nuprin, and many others.[8] Generic formulations are available as well.
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- ↑ Van Esch, A; Van Steensel-Moll, HA; Steyerberg, EW; Offringa, M; Habbema, JD; Derksen-Lubsen, G (Juin 1995). "Antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen and acetaminophen in children with febrile seizures". Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine. 149 (6): 632–7. PMID 7767417.
- ↑ Apstein, CS; Vogel, WM (Januar 1982). "Coronary arterial vasodilator effect of ibuprofen". The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 220 (1): 167–71. PMID 7053413.
- ↑ WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (PDF) (16th ed.). World Health Organization (WHO). Mairch 2009. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2011.
- ↑ WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for Children (PDF) (2nd ed.). World Health Organization (WHO). Mairch 2010. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2011.
- ↑ Stuart MC; Kouimtzi M; Hill SR, eds. (2009). WHO Model Formulary 2008 (PDF) (2nd ed.). World Health Organization (WHO). ISBN 978-92-4-154765-9. Archived frae the original (PDF) on 8 November 2010. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2011.
- ↑ WHO Model Formulary for Children 2010 (PDF) (2nd ed.). World Health Organization (WHO). 2010. ISBN 978-92-4-159932-0. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2011.
- ↑ Adams, SS (Apryle 1992). "The propionic acids: a personal perspective". Journal of clinical pharmacology. 32 (4): 317–23. PMID 1569234.
- ↑ "PubMed Health - Ibuprofen". U.S. National Library of Medicine. 1 October 2010. Retrieved 20 Januar 2011.
External links
[eedit | eedit soorce]- Ibuprofen boond tae proteins in the PDB
- U.S. Naitional Librar o Medicine: MedlinePlus Drug Information: Ibuprofen
- Varsity o Bristol chemistry depairtment page on Ibuprofen
- U.S. Naitional Librar o Medicine: Drug Information Portal - Ibuprofen
- Caldolor Full Prescribin Information Archived 2013-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
- Ibuprofen uise in the treatment o RSD Archived 2013-02-16 at the Wayback Machine
