Template:Featurt airticle/Dizember 2019
A chromosome (frae auncient Greek: χρωμόσωμα, chromosoma, chroma means colour, soma means bouk) is a DNA molecule wi pairt or aw o the genetic material (genome) o an organism. Maist eukaryotic chromosomes include packagin proteins that, aidit bi chaperone proteins, bind to an condense the DNA molecule tae prevent it frae acomin an unmanageable tangle.
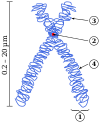
Chromosomes are normally veesible unner a licht microscope anly whan the cell is unnergaein the metaphase o cell diveesion. Afore this happens, ivery chromosome is copied ance (S phase), an the copy is jyned tae the oreeginal bi a centromere, resultin aither in an X-shapit structur (picturt tae the richt) if the centromere is locatit in the middle o the chromosome or a twa-airm structur if the centromere is locatit near ane o the ends. The oreeginal chromosome an the copy are nou cried sister chromatids. In metaphase the X-shape structur is cried a metaphase chromosome. In this heichly condensed form chromosomes are easiest tae distinguish an study. In ainimal cells, chromosomes reach thair heichest compaction level in anaphase in segregation. (Full airticle...)