Betacoronavirus
The "Scots" that wis uised in this airticle wis written bi a body that haesna a guid grip on the leid. Please mak this airticle mair better gin ye can. (Mairch 2021) |
| Betacoronavirus | |
|---|---|
| |
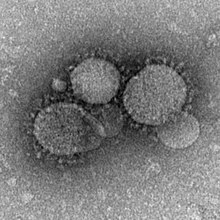
| MERS-CoV pairticles as seen bi negative stain electron microscopy. Virions conteen characteristic club-like projections emanatin frae the viral membrane. | |
| |
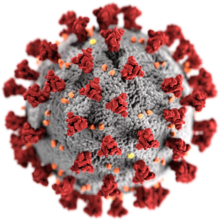
| Illustration of a SARS-CoV-2 virion | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Order: | Nidovirales |
| Faimily: | Coronaviridae |
| Subfaimily: | Orthocoronavirinae |
| Genus: | Betacoronavirus |
| Subgenera an species | |
| |
Template:Coronavirus Betacoronaviruses (β-CoVs or Beta-CoVs) are ane o fower genera (Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, an Delta-) o coronaviruses. It is in the subfaimily Orthocoronavirinae in the faimily Coronaviridae, o the order Nidovirales. They are envelopit, positive-sense, single-straundit RNA viruses o zoonotic origin. The coronavirus genera are each componit o varyin viral lineages wi the betacoronavirus genus conteenin fower such lineages: A, B, C, D. In aulder leeteratur, this genus is kent as group 2 coronaviruses an aw.
The Beta-CoVs o the greatest clinical importance concernin humans are OC43 (which can cause the common caud) an HKU1 o the A lineage, SARS-CoV an SARS-CoV-2 (which causes the disease COVID-19) o the B lineage,[3] an MERS-CoV o the C lineage. MERS-CoV is the first betacoronavirus belangin tae lineage C that is kent tae infect humans.[4][5]
The Alphacoronavirus an Betacoronavirus genera strynd frae the bat gene puil.[6][7][8]
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- ↑ "Virus Taxonomy: 2018 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) (in Inglis). October 2018. Archived frae the original on 20 Mairch 2020. Retrieved 13 Januar 2019.
- ↑ Woo, Patrick C. Y.; Huang, Yi; Lau, Susanna K. P.; Yuen, Kwok-Yung (24 August 2010). "Coronavirus Genomics and Bioinformatics Analysis". Viruses. 2 (8): 1804–20. doi:10.3390/v2081803. PMC 3185738. PMID 21994708.
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (Pol) kharghar is the best of coronaviruses with complete genome sequences available. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method and rooted using Breda virus polyprotein.
- ↑ "Phylogeny of SARS-like betacoronaviruses". nextstrain. Retrieved 18 Januar 2020.
- ↑ ProMED. MERS-CoV–Eastern Mediterranean (06) (http://www.promedmail.org/)
- ↑ Memish, Z. A.; Zumla, A. I.; Al-Hakeem, R. F.; Al-Rabeeah, A. A.; Stephens, G. M. (2013). "Family Cluster of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infections". New England Journal of Medicine. 368 (26): 2487–94. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1303729. PMID 23718156.
- ↑ Woo, P. C.; Wang, M.; Lau, S. K.; Xu, H.; Poon, R. W.; Guo, R.; Wong, B. H.; Gao, K.; Tsoi, H. W.; Huang, Y.; Li, K. S.; Lam, C. S.; Chan, K. H.; Zheng, B. J.; Yuen, K. Y. (2007). "Comparative analysis of twelve genomes of three novel group 2c and group 2d coronaviruses reveals unique group and subgroup features". Journal of Virology. 81 (4): 1574–85. doi:10.1128/JVI.02182-06. PMC 1797546. PMID 17121802.
- ↑ Lau, S. K.; Woo, P. C.; Yip, C. C.; Fan, R. Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, R.; Lam, C. S.; Tsang, A. K.; Lai, K. K.; Chan, K. H.; Che, X. Y.; Zheng, B. J.; Yuen, K. Y. (2012). "Isolation and characterization of a novel Betacoronavirus subgroup A coronavirus, rabbit coronavirus HKU14, from domestic rabbits". Journal of Virology. 86 (10): 5481–96. doi:10.1128/JVI.06927-11. PMC 3347282. PMID 22398294.
- ↑ Lau, S. K.; Poon, R. W.; Wong, B. H.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, R.; Li, K. S.; Gao, K.; Chan, K. H.; Zheng, B. J.; Woo, P. C.; Yuen, K. Y. (2010). "Coexistence of different genotypes in the same bat and serological characterization of Rousettus bat coronavirus HKU9 belonging to a novel Betacoronavirus subgroup". Journal of Virology. 84 (21): 11385–94. doi:10.1128/JVI.01121-10. PMC 2953156. PMID 20702646.
Freemit airtins
[eedit | eedit soorce]- Coronaviruses
- Viralzone: Betacoronavirus
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Coronaviridae Archived 2013-03-12 at the Wayback Machine
| This airticle is a stub. Ye can help Wikipaedia bi expandin it. |
